PP2: Global Media
In recent years, the global workforce has undergone a profound transformation, driven by advancements in technology, shifting economic priorities, and evolving worker preferences. Traditional employment structures, once characterized by long-term, full-time positions with stable benefits, are rapidly giving way to more flexible work arrangements. Remote work, freelancing, and the gig economy have emerged as dominant trends, offering workers greater autonomy while posing new challenges for businesses and policymakers. This shift is reshaping industries, redefining career paths, and influencing how people engage with work in the modern era.
Remote work has seen an unprecedented surge, particularly following the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated the adoption of digital collaboration tools. Companies around the world have embraced hybrid and fully remote work models, allowing employees to work from locations of their choosing. This shift has not only increased productivity in many cases but has also expanded the talent pool, enabling organizations to hire workers from different regions and countries. Employees, in turn, have benefited from improved work-life balance and reduced commuting costs. However, remote work also presents challenges, such as maintaining company culture, ensuring cybersecurity, and addressing concerns about employee isolation. As businesses refine remote work policies, the long-term impact on workplace dynamics will continue to unfold.
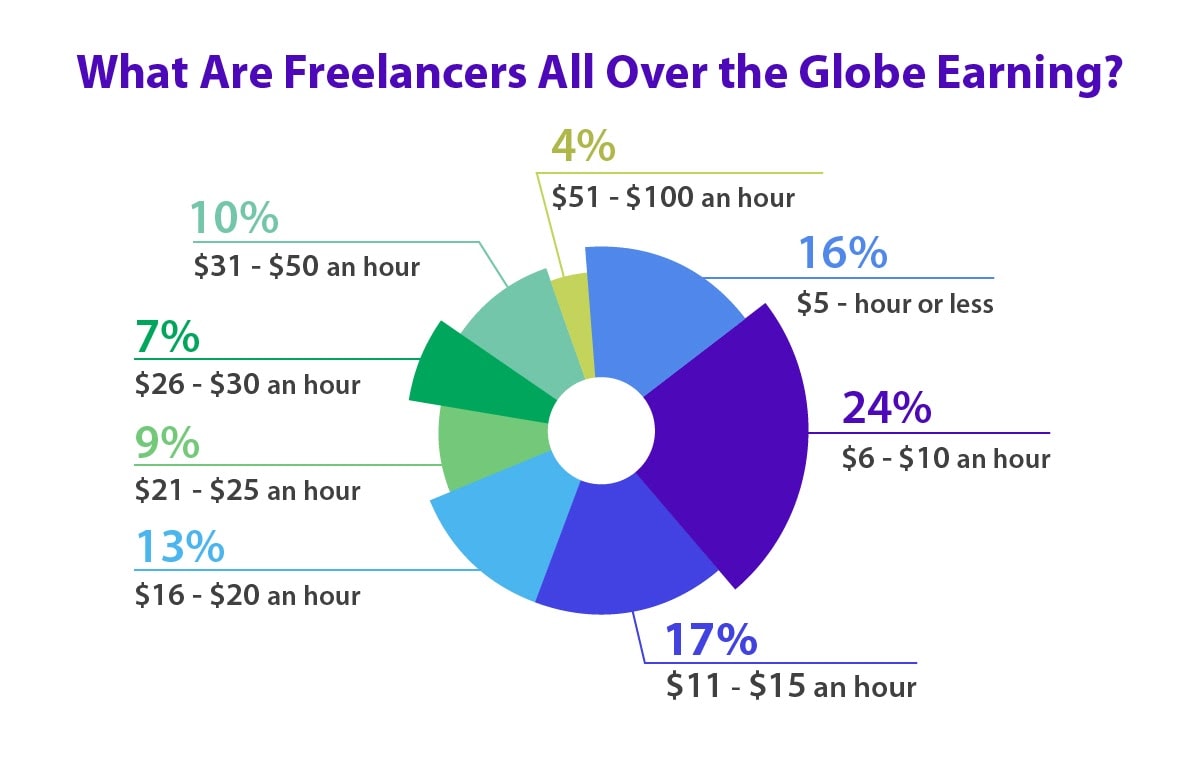
The gig economy, characterized by short-term, on-demand jobs, has reshaped employment landscapes across various sectors. Companies like Uber, DoorDash, and TaskRabbit have created platforms where workers can take on temporary jobs with flexible schedules. While the gig economy provides individuals with opportunities to earn income on their own terms, it also raises concerns regarding job security, benefits, and labor rights. Unlike traditional employees, gig workers often do not receive health insurance, retirement plans, or paid leave, leading to ongoing debates about labor protections and the need for updated employment regulations. Governments worldwide are grappling with how to balance the benefits of gig work with the rights and well-being of workers in this evolving labor market.
(Link in Image)
As remote work, freelancing, and the gig economy continue to expand, traditional employment models are being redefined. Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid work models, offering project-based contracts, and integrating more flexible employment arrangements. This shift is prompting policymakers to reconsider labor laws, focusing on ways to provide benefits and protections for non-traditional workers. Education and skill development will also play a crucial role, as workers must continuously adapt to new technologies and changing market demands.

Comments
Post a Comment